Drupal 9, the latest version of the popular open-source content management system, was released on June 3rd. This new version includes many new features and lays an important foundation for the future of the platform (more on that later). But, just as importantly, it means that Drupal 7 and 8 will no longer be supported in the relatively near future.
For Drupal 8, support will end on Nov. 28, 2021, because the technology Drupal 8 is built on, Symfony-3, is also reaching its end-of-life on that date. Support for Drupal 7 will end after Nov. 28, 2022. That date is actually one year later than originally planned; upon initial release, Drupal planned to end its support in November of 2021, but the company pushed that cutoff back due to COVID-19’s impact on business budgets and the subsequent lack of resources to make the necessary upgrades (note: an earlier version of this article reflected the shared cutoff dates of both platforms).
With those older versions of Drupal being retired, the Drupal community will stop maintaining and supporting the core product and any of the contributed modules. After those cutoff dates, there will be security vulnerabilities, incompatibilities with browser updates, and other bugs that will not be addressed.
Essentially, this means that websites built on these older platforms will become increasingly vulnerable to attacks, and users may start seeing functional or display issues. The next steps are clear: It is strongly recommended that every Drupal 7 or 8 website upgrade prior to their respective cutoff dates of support. Luckily, there is plenty of time to start planning and consider your options.
How to Find Out What Version of Drupal Your Site Is On
First, if you aren’t sure what version of Drupal you’re on, it’s pretty easy to find out. After you’ve logged in to the admin, go to Administration > Reports > Status Report. At the very top of the table you’ll see a field that lists the Drupal version number for your site (and much more information about your specific Drupal instance). You can usually find this at yourdomain.com/admin/reports/status
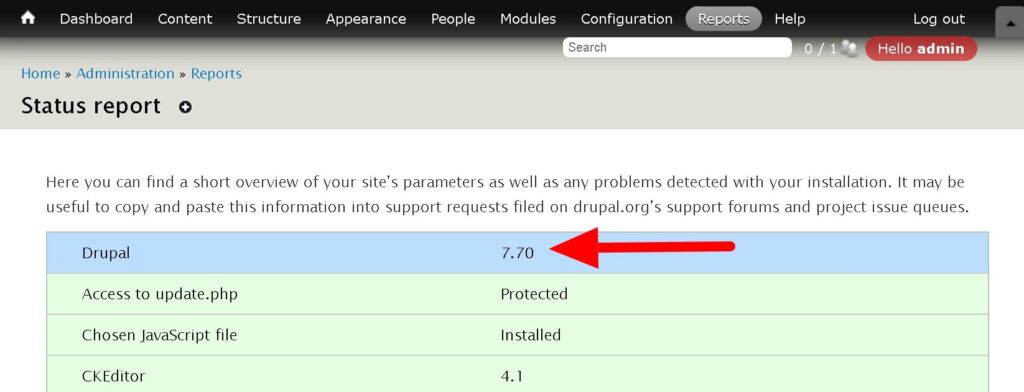
If your status report says your Drupal version starts with 8.xx or 7.xx (or anything lower), keep reading to learn what should do next.
What to Do If Your Website Is On Drupal 7
If your website is on Drupal 7, you should start planning to make an upgrade now. A transition from D7 to D9 will be challenging, as compatibility issues may limit your options.
If it’s feasible, a complete website redesign might be in your best interests. Starting from scratch in Drupal 9 (or another CMS) will allow you to rethink your site architecture while ensuring security and compatibility.
However, if you’re determined to try an upgrade, you can start by migrating your content and code up to Drupal 8 first. You’ll want to check for the availability of your modules in Drupal 8 using the Upgrade Status Drupal module. The Drupal Module Upgrader may also help with the upgrade. Once you’ve updated to D8, you’ll need to remove any deprecated code before finally upgrading to D9.
What to Do If Your Website Is On Drupal 8
If you’re already on Drupal 8, you should have a much easier time updating your core from Drupal 8 to 9. In fact, one of the standout features of Drupal 9 is its backwards compatibility with D8 and its ability to provide an easy upgrade process. This means that all your D8 components will still work in D9. And if you are using contributed modules, you will be able to upgrade those as soon as the updates are available.
Make sure you are not using any deprecated modules and APIs, and where possible, that you are using the latest versions of dependencies. If you do that, your upgrade will be relatively easy.
Just make sure you make the upgrade prior to November of 2021, if you’re on Drupal 8, and prior to November of 2022, if you’re on Drupal 7.
What’s new in Drupal 9?
Unlike other major Drupal upgrades, Drupal 9 is not a complete reinvention of Drupal. In fact, it is mostly built in Drupal 8, with a few updates to core features and the removal of some depreciated code. That said, it does have some new features worth noting:
- Backwards Compatibility
This is more of a philosophical shift than a feature, but it’s important nonetheless. This means that after Drupal 9, all subsequent releases will be relatively easy and painless. If you have suffered through the upgrade from D7 to D8, this will be welcome news. - Improved Site Performance
A new caching system allows for faster page load times. - Simplified Content Tools
A new page layout builder, content workflow tools, and media management system will be a welcome change for site admins. - Media Management
Admins can upload images and files like they always have, but can now include third party media such as YouTube and Vimeo links, as well.
Will users notice a difference?
Since Drupal 9 is technically a minor update to D8, chances are your users won’t notice any big changes. But the platform’s upgraded performance and a mobile-first approach may help improve site performance.
Summary
In the end, any content management system is only as good as how well it is architected and built for the needs of site admins and users. Drupal 9 provides several foundational updates that should help everyone manage and update their websites going forward.